Best Injection Molding Costs Guide for Manufacturers?
Understanding injection molding costs is crucial for manufacturers. It influences budgeting and pricing strategies. Many factors contribute to these costs, including material choice and production volume.
Injection molding is not just a technique; it’s an investment. The price per part decreases with larger production runs. However, initial setup costs can be high. This duality often leads to confusion.
Navigating these expenses requires careful planning. Overlooking cost factors can impact profitability. Manufacturers must analyze their needs and market conditions. It's vital to balance quality and efficiency in this process. Reflecting on past projects can help in making better decisions.

Understanding Injection Molding: An Overview of the Process and Costs
Injection molding is a key process in manufacturing. It transforms raw plastic into finished products. The costs involved can vary significantly. Factors include material type, part complexity, and production volume. A recent industry report highlights that material costs can account for up to 40% of total expenses.
Mold design and fabrication add another layer of expense. A simple mold may cost around $5,000. However, complex molds can exceed $50,000. These costs can be daunting for small manufacturers. Yet, understanding the process can lead to savvy decisions. Quality molds, although expensive, often yield better precision and durability.
Production costs also fluctuate based on volume. High-volume runs can reduce unit costs dramatically. The savings can be significant. That said, initial investments in molds and materials can pose risks. It’s essential to calculate all potential costs accurately. Short-sightedness here can lead to financial strain later. Balancing these elements is crucial for profitability.
Key Factors Influencing Injection Molding Costs: Materials and Labor
The cost of injection molding is influenced by various factors, especially materials and labor. Selecting the right material is crucial. Different plastics can have varying costs. For example, common thermoplastics may be less expensive than high-performance polymers. This might seem obvious, but many manufacturers overlook this aspect. They choose materials based solely on the final product's requirements, ignoring the initial cost implications.
Labor costs also play a significant role in the total expense of injection molding. Skilled workers are essential for operating machinery and achieving precision. The labor market varies by location. In some areas, skilled labor is plentiful and affordable. In others, it can be a significant expense. Additionally, fluctuations in labor costs can lead to unexpected budget overruns. Manufacturers must consider both direct and indirect labor costs in their calculations.
Understanding these factors is vital for budgeting effectively. However, many get it wrong. They either underestimate the material costs or overlook fluctuating labor rates. This oversight can lead to frustration when projects exceed their budgets. An honest assessment of all cost elements is necessary for effective planning.
Best Injection Molding Costs Guide for Manufacturers
| Factor | Description | Estimated Cost Impact (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Cost varies significantly based on the type of plastic used, e.g., ABS, PS, POM, etc. | 30-50% |
| Labor Cost | Costs associated with skilled labor for machine operation and maintenance. | 10-20% |
| Machine Setup | Costs incurred in setting up the machinery for production runs. | 5-15% |
| Cycle Time | Length of time needed for each production cycle affects throughput. | 10-30% |
| Volume of Production | Higher volumes can reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. | 25-40% |
Average Cost Breakdown: From Machine Operation to Tooling Expenses
When considering injection molding, understanding the cost breakdown is crucial. There are multiple elements that contribute to the total expenses. Machine operation is a significant factor. The energy consumption of the equipment impacts the overall costs. Regular maintenance also adds to these expenses. It's not just about the purchase price of the machinery.
Tooling expenses often present a hidden challenge. Custom molds can be expensive depending on the complexity. The design process itself can lead to unforeseen costs. Many manufacturers find it difficult to predict these expenses accurately. A well-planned tooling strategy can mitigate some of these issues. However, unexpected changes during production can drive costs higher than anticipated.
Material costs are another piece of the puzzle. Resin prices fluctuate based on market demands and availability. This variability makes budgeting for materials tricky. Additionally, quality and type of material directly influence the final product's performance. Manufacturers must balance cost with quality. It's a constant struggle to achieve the right combination for profitability. Each of these factors requires careful analysis and foresight.
Cost Comparisons: Injection Molding vs. Alternative Manufacturing Methods
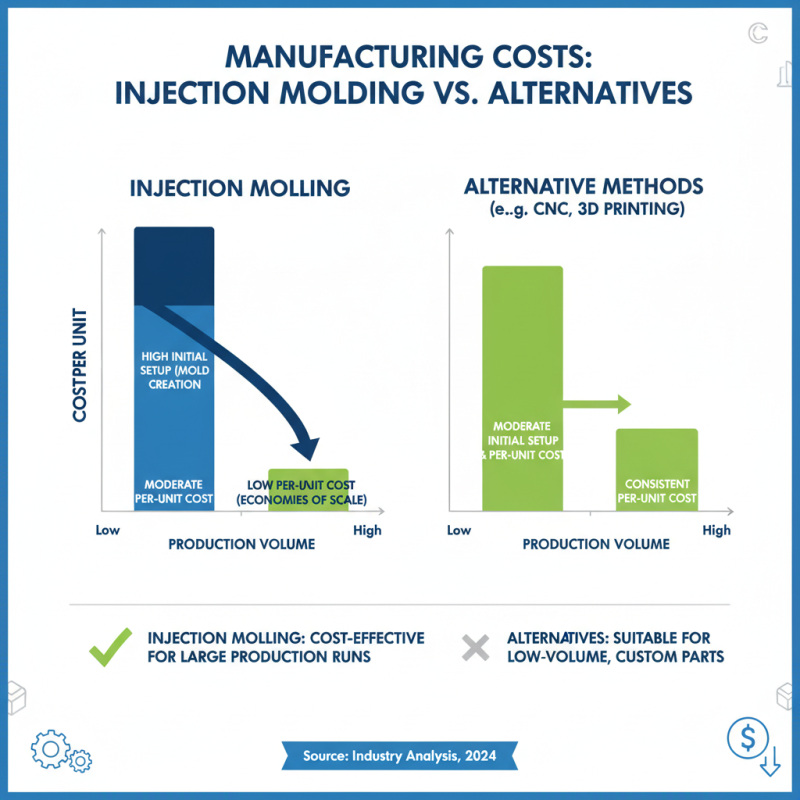
When comparing injection molding with alternative manufacturing methods, costs can vary significantly. Injection molding is often seen as a more cost-effective solution for large production runs. The initial setup costs, including mold creation, can be high. However, once the molds are in place, the price per unit dramatically decreases. This is especially beneficial for high-volume production.
On the other hand, alternative methods like 3D printing or CNC machining have different expense structures. They offer flexibility and quicker prototyping but can be more costly for mass production. For small quantities, these methods might be financially viable. Yet, as order sizes increase, injection molding tends to become the cheaper option.
While injection molding has clear advantages, it is not without its challenges. The initial investment can be daunting. Additionally, design changes after mold creation can incur high costs. This aspect requires careful planning and consideration. Manufacturers must weigh their options, balancing upfront costs against long-term savings to determine the best method for their needs.
Strategies for Reducing Injection Molding Costs Without Sacrificing Quality
Reducing injection molding costs is vital for manufacturers. There are practical strategies you can implement. Focus on design optimization first. A simpler design often uses less material and time. It can lead to significant savings. Aim for minimal complexity while maintaining functionality.
Tip: Use software for mold flow analysis. This can help identify potential issues early. Addressing these in the design phase saves time later. Also, consider the materials you use. Alternative materials can sometimes be more cost-effective. Evaluate the properties you truly need to meet your quality standards.
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can also impact costs. Negotiate pricing based on volume. Ask about bulk discounts. However, ensure that reduced costs do not compromise quality. Quality failures can lead to higher costs in the long run, affecting your production cycle.
Tip: Regularly review your production process. Look for areas where you can cut down waste. Small adjustments can lead to larger savings. Remember that constant reflection on your processes is necessary for improvement.
Related Posts
-
Understanding Injection Molding Costs: Key Factors Impacting 2025 Prices
-

7 Essential Tips for Sourcing Plastic Parts Globally
-
Top Injection Molding Tooling Techniques for Efficient Production?
-

Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Design for Injection Molding in 2025
-

Ultimate Guide to Selecting the Right Injection Molding Tooling for Your Business Needs
-

Unveiling the Advantages of Polypropylene Plastic: A Game Changer for Modern Manufacturing
