How to Choose the Right Injection Molding Tooling for Your Project
Injection molding tooling is a critical component in the manufacturing process, directly impacting both product quality and production efficiency. According to a recent report by the American Society of Plastic Engineers, the global injection molding market is expected to reach $300 billion by 2025, underscoring the growing reliance on effective tooling solutions. Selecting the right injection molding tooling not only optimizes production costs but also enhances the final product's performance in the competitive marketplace.
Expert insights further emphasize the importance of this decision. John Davis, a leading authority in the injection molding sector, states, “The selection of appropriate injection molding tooling can determine the success or failure of a project, as it influences everything from design complexities to cycle times.” His perspective highlights the necessity for businesses to carefully evaluate their tooling options. Whether you are developing a new prototype or scaling up for mass production, understanding the key factors involved in selecting injection molding tooling will ensure that your manufacturing process runs smoothly and cost-effectively.

Understanding the Basics of Injection Molding Tooling
Injection molding tooling is a crucial component in the manufacturing process, dictating the efficiency and quality of the final product. To select the right tooling for your project, it is essential to first grasp the fundamental principles of injection molding. The process involves the injection of molten plastic material into a pre-designed mold, which then cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Understanding how this process works helps in determining the specific requirements for the tooling, such as material type, mold design, and cycle time.
Key factors to take into consideration include the complexity of the part design, the type of material to be used, and the anticipated production volume. Complex designs may require more intricate tooling solutions, while simpler designs can often be accommodated by standard molds. Additionally, different materials have varying melting temperatures and cooling rates, influencing the choice of tooling materials and designs. High production rates necessitate robust tooling to withstand repeated use without significant wear, while lower volumes might allow for more cost-effective options. By carefully assessing these factors, one can ensure that the chosen injection molding tooling aligns with project goals and operational needs.
Injection Molding Tooling Cost Comparison
Identifying Project Requirements for Optimal Tool Selection
When it comes to selecting the right injection molding tooling for your project, understanding your project requirements is essential. Initial considerations should include the materials you plan to use, the desired production volume, and the complexity of the part geometry. Each of these factors will directly influence the design and type of tooling required. For instance, high-volume production might necessitate more durable tools, while complex parts might require specialized features that can affect tooling costs.
**Tips:** Clearly define the specifications and functionality of the molded parts before diving into tooling options. This clarity aids in identifying which tooling material—such as steel or aluminum—will best suit your needs based on durability and cost-efficiency. Additionally, engage with your design and engineering teams early in the process to incorporate feedback and optimize the tooling design for manufacturability.
Another crucial aspect is the timeline for your project. The urgency of production can significantly affect tooling choices, as some tooling types offer quicker lead times than others. Understanding the trade-offs between speed, quality, and costs can help in making informed decisions.
**Tips:** Always have a contingency plan for delays; having a backup supplier or alternative tooling option can save time and resources in case of unexpected challenges. Engage in thorough testing and validation of your tooling before full-scale production to avoid costly revisions later.
Evaluating Material Compatibility with Injection Molding Processes
When selecting the right tooling for injection molding projects, evaluating material compatibility is a crucial step. Different plastics and composites exhibit varying behaviors during the injection molding process, including melting points, viscosity, and shrinkage rates. Understanding the characteristics of the material you're working with can help avoid potential issues such as warping, poor surface finish, or difficulties in mold release. It's essential to choose tooling that can accommodate the specific thermal and mechanical properties of the material, ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications.
Another important aspect of material compatibility is the interaction between the injection molded part and the tooling itself. Certain materials may require tooling made from specific metals or coatings to prevent wear and degradation during repeated cycles. For instance, abrasive materials might necessitate harder or more durable tooling materials to extend service life. Additionally, the chemical resistance of the tooling to the injected materials is vital, especially for applications involving corrosive compounds. By thoroughly evaluating these factors, you can select the appropriate tooling that enhances both the efficiency of the injection molding process and the quality of the final product.
How to Choose the Right Injection Molding Tooling for Your Project - Evaluating Material Compatibility with Injection Molding Processes
| Material Type | Compatibility with Injection Molding | Processing Temperature (°C) | Strength (MPa) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Excellent | 200-230 | 30-40 | Containers, automotive parts |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Good | 220-240 | 40-60 | Consumer electronics, toys |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Good | 180-220 | 20-35 | Packaging, bottles |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Excellent | 250-280 | 60-70 | Optical discs, safety goggles |
| Nylon (PA) | Good | 230-270 | 50-80 | Gears, automotive applications |
Exploring Different Types of Injection Molding Tools and Their Applications
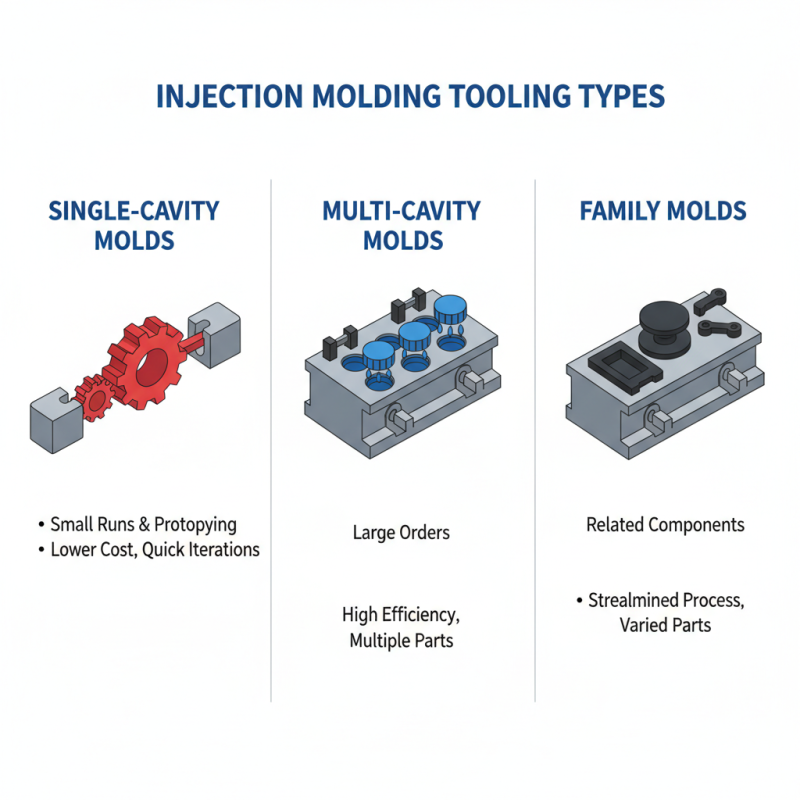
When selecting injection molding tooling for your project, understanding the different types available and their specific applications is crucial. For instance, **single-cavity molds** are ideal for small production runs and prototyping, allowing for quick iterations and lower initial costs. **Multi-cavity molds**, on the other hand, enhance production efficiency by enabling multiple parts to be produced in a single cycle, making them suitable for larger orders. Additionally, **family molds**, which produce different parts in one cycle, can streamline processes when creating related components.
Tips: Before making a decision, consider the material you will be using in your project. Certain tools are better suited for specific materials, affecting the quality of the finished product. It’s also essential to evaluate the complexity of your design; more intricate shapes may require specialized tooling options, which can impact both time and cost.
Another type to consider is **hot runner systems**, which help reduce waste and improve production efficiency by keeping the plastic in a molten state. This technique is beneficial for thermoplastic materials and can save time during the molding process. Always analyze the trade-offs between the initial investment and long-term benefits when choosing the right tooling for your needs.
Assessing Cost and Production Efficiency in Tooling Decisions
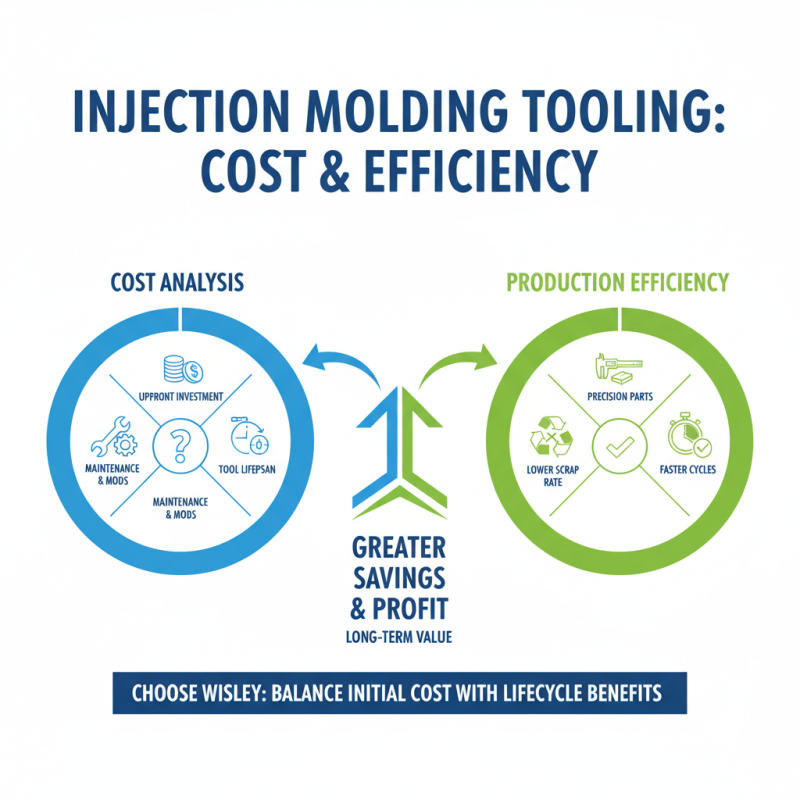
When selecting the right injection molding tooling for your project, assessing cost and production efficiency is crucial. The initial cost of tooling can vary significantly depending on complexity, material, and manufacturing processes. It is essential to conduct a thorough cost analysis, which includes not only the upfront tooling investment but also the long-term operating costs. These may encompass maintenance, potential modifications, and the lifespan of the tool. A high-cost tool may seem less attractive initially, but if it produces parts with higher precision and lower scrap rates, it can ultimately lead to greater savings and efficiency over time.
In addition to cost considerations, production efficiency plays a significant role in tooling decisions. A well-designed tool can enhance cycle times, reduce downtime, and improve overall throughput. Evaluating factors such as part design, material choice, and the level of automation can contribute to more efficient production. Tools that allow for rapid changeovers or integrate advanced features such as hot runner systems can further enhance productivity. Therefore, striking a balance between upfront costs and long-term operational efficiency is critical in making informed tooling decisions that align with project goals.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Injection Moulding Process Examples That Drive Global Procurement Efficiency
-

What is Low Cost Injection Molding and How it Revolutionizes Manufacturing Efficiency
-

Exploring Trends in Injection Molding Materials at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

Unlocking the Secrets of Low Cost Injection Molding: A Comprehensive Guide for Innovators
-

Innovative Techniques for Optimizing Design for Injection Molding in Modern Manufacturing
-

How to Optimize PVC Injection Molding for Maximum Efficiency and Quality
