What is a Plastic Sheet and its Uses in Various Industries
Plastic sheets are ubiquitous materials that play a vital role across a multitude of industries, contributing significantly to manufacturing processes and product development. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global plastic sheets market was valued at approximately $33.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by the versatility and durability of plastic sheets, which are utilized in sectors ranging from construction to packaging.
In the construction industry, plastic sheets are commonly employed for moisture barriers, insulating materials, and protective coverings. They serve essential functions, such as preventing water infiltration and reducing heat loss, thereby enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Meanwhile, in the packaging sector, plastic sheets are indispensable for creating lightweight, durable, and cost-effective solutions that cater to the growing demand for sustainable packaging options. This demonstrates the significance of plastic sheets in fostering innovation and sustainability within various industries, making them a critical component of modern production and operational strategies.

Definition and Composition of Plastic Sheets
Plastic sheets are versatile materials composed primarily of synthetic polymers, such as polyethylene, polycarbonate, or acrylic. These polymers are created through chemical processes that transform raw materials into durable, flexible sheets suitable for various applications. The composition of plastic sheets may include additives to enhance properties like UV resistance, flame retardance, or impact strength, which contribute to their functionality across different industries.
In many applications, thickness and texture can vary, making plastic sheets adaptable for specific needs. For example, in the construction industry, thick polycarbonate sheets are often used for roofing and glazing due to their transparency and strength, while thinner sheets can be employed in packaging and advertising displays. The versatility of plastic sheets also extends to the automotive sector, where they serve as lightweight components that contribute to fuel efficiency. Overall, the tailored composition of plastic sheets allows them to be utilized effectively in diverse fields, ranging from agriculture to electronics, each benefiting from their unique characteristics.
What is a Plastic Sheet and its Uses in Various Industries - Definition and Composition of Plastic Sheets
| Material Type | Common Usage | Thickness (mm) | Industry | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Packaging Films | 0.1 - 0.5 | Packaging Industry | Lightweight, Moisture-resistant |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Construction Materials | 1 - 5 | Construction Industry | Durable, Weather-resistant |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Safety Glasses, Roof Panels | 2 - 10 | Manufacturing Industry | Impact-resistant, Transparent |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | Display Cases, Lighting Fixtures | 3 - 12 | Retail Industry | Crystal Clear, UV-resistant |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Food Packaging, Disposable Utensils | 0.5 - 2 | Food Industry | Cost-effective, Lightweight |
Common Types of Plastic Sheets and Their Properties
Plastic sheets are versatile materials widely used across various industries due to their unique properties. Among the most common types of plastic sheets are polycarbonate, acrylic, and PVC. Each type exhibits distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
Polycarbonate sheets are renowned for their strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for safety applications such as protective barriers and safety glazing. They also have excellent optical clarity, making them a preferred choice for transparent applications like skylights and displays. Acrylic sheets, on the other hand, are lighter than glass and have exceptional clarity. They are frequently used in signage, displays, and aquariums due to their ability to transmit light effectively while being shatter-resistant.
PVC sheets offer durability and resistance to chemicals, making them suitable for a range of applications, from construction to medical settings. Their flexibility and ease of fabrication allow for various shapes and designs, which is beneficial in manufacturing components, cladding, and indoor furniture. Each of these plastic sheet types serves specific needs across industries, demonstrating their importance in modern applications.
Applications of Plastic Sheets in the Construction Industry
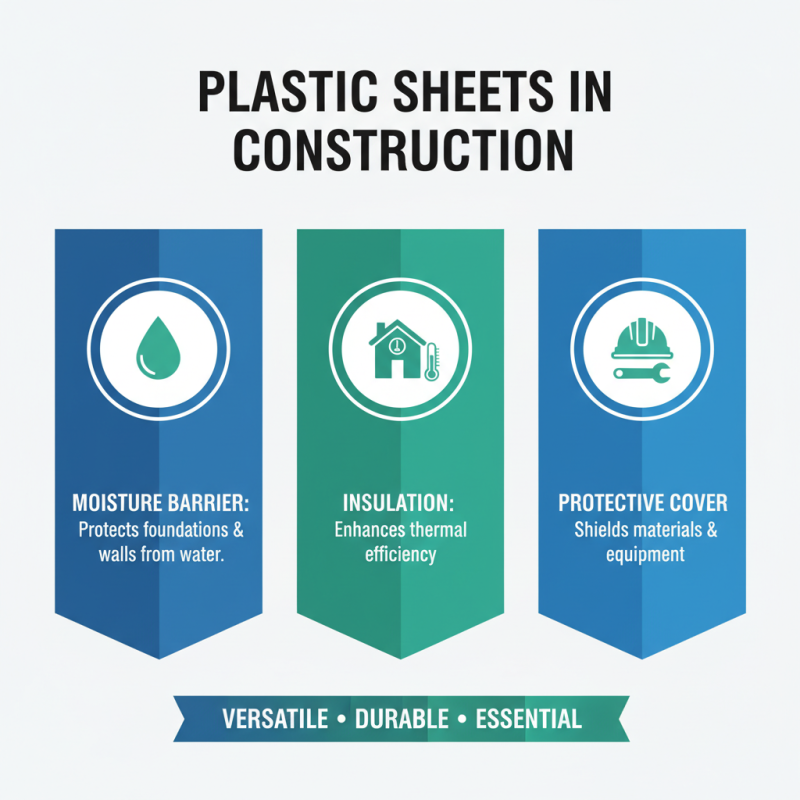
Plastic sheets have become an essential material in the construction industry due to their versatility and durability. These sheets are used in a variety of ways, ranging from protective barriers to insulation materials. In construction, plastic sheets can serve as moisture barriers, preventing the penetration of water and contributing to the integrity of structures. They can be laid down before pouring concrete to protect it from moisture from the ground, ensuring a solid foundation.
Additionally, plastic sheets are widely utilized for temporary protection of surfaces during construction. They can cover floors, walls, and furniture to shield them from dust, paint, and other debris generated during building activities. Their lightweight nature and ease of handling make them a go-to choice for contractors aiming to maintain a clean work environment. Furthermore, plastic sheets are also employed in forming molds for concrete, where their flexibility allows for creating intricate designs while ensuring that the final product maintains its shape. This adaptability highlights the importance of plastic sheets in enhancing efficiency and safety in various construction processes.
Roles of Plastic Sheets in Packaging and Shipping
Plastic sheets are versatile materials that have become essential in the packaging and shipping industries. One of the primary roles of plastic sheets in packaging is to provide a protective barrier for products during transit. They are lightweight yet durable, making them an ideal choice for safeguarding items from dust, moisture, and physical damage. This is particularly crucial in sectors such as food, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, where maintaining product integrity is paramount. The use of plastic sheets not only enhances the longevity of goods but also helps in preserving their quality until they reach the end consumer.
In addition to protection, plastic sheets also contribute to efficient logistics. They can be easily cut, shaped, and customized to fit various packaging needs. For instance, they are often used to create liners for pallets and containers, helping to optimize space and reduce the risk of damage during handling and transportation. Moreover, plastic sheets can be recycled, making them an environmentally friendly option when managed properly. Their adaptability and strength ensure that they remain a vital component in contemporary packaging solutions, addressing both functional and sustainable needs in the shipping process.
Plastic Sheet Uses Across Various Industries
Innovative Uses of Plastic Sheets in the Medical and Automotive Sectors
Plastic sheets are versatile materials used across various industries, particularly in the medical and automotive sectors. In the medical field, plastic sheets serve critical roles in everything from protective equipment to packaging. For instance, a report by Grand View Research indicates that the global market for medical plastics is projected to reach $45 billion by 2026, reflecting an increased demand for durable, sterile materials in healthcare applications. Plastic sheets, such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), are commonly used for sterile barriers, which protect medical devices and instruments from contamination. Their lightweight nature, along with ease of sterilization, makes them ideal for surgical drapes and covers.
In the automotive industry, plastic sheets are increasingly utilized for their ability to enhance performance while reducing weight. According to a study by MarketsandMarkets, the automotive plastics market is expected to grow from $26.1 billion in 2022 to $37.6 billion by 2027. Plastic sheets are often used in car interiors for dashboards, door panels, and other components. Their use leads to improved fuel efficiency due to weight reduction, which is crucial as manufacturers strive to meet stringent emissions regulations. Additionally, advancements in plastic technology have allowed for better heat and sound insulation, making vehicles more comfortable and environmentally friendly. The innovative applications of plastic sheets exemplify the material's adaptability and value across these dynamic industries.
Related Posts
-

What is the Role of Plastic Sheets in Modern Industries
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Plastic Caps for Packaging and Their Market Growth Insights
-

7 Essential Tips for Sourcing Plastic Parts Globally
-

Exploring the Versatility of PVC Sheets: Innovative Applications You Didn't Know About
-

Top 10 Benefits of Injection Molding for Manufacturing Efficiency
-

How to Optimize Your Process for Polypropylene Injection Molding Success
