Exploring the Versatility of PVC Material: Applications, Benefits, and Environmental Impact
PVC material, known for its exceptional versatility and durability, has become a cornerstone in various industries, ranging from construction to healthcare.
According to a report by the Plastics Industry Association, the global demand for PVC is expected to reach 42 million metric tons by 2025, reflecting its growing significance in modern applications.
This synthetic polymer not only offers an excellent balance of performance and cost-effectiveness but also contributes to sustainability initiatives, as recycling processes for PVC are becoming increasingly efficient.
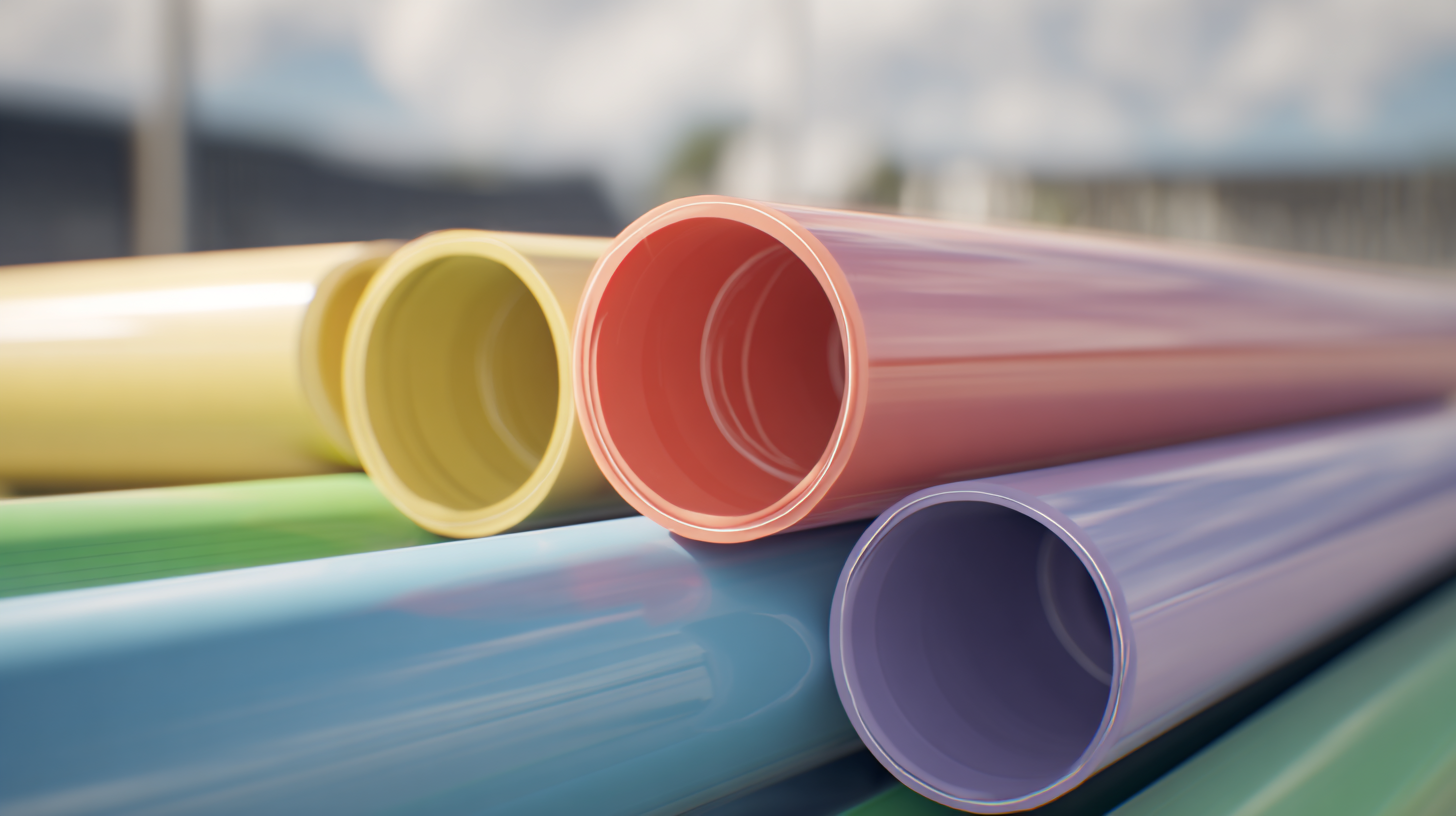 Products made from PVC material, such as pipes, flooring, and medical devices, showcase its adaptability while meeting regulatory standards for safety.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions that align with environmental goals, understanding the applications, benefits, and impacts of PVC material is crucial for paving the way towards a more sustainable future.
Products made from PVC material, such as pipes, flooring, and medical devices, showcase its adaptability while meeting regulatory standards for safety.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions that align with environmental goals, understanding the applications, benefits, and impacts of PVC material is crucial for paving the way towards a more sustainable future.
Understanding the Composition and Properties of PVC Material
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a widely used plastic known for its versatility and practicality across various applications. Composed of vinyl chloride monomers, PVC exhibits excellent durability, chemical resistance, and low thermal conductivity, making it suitable for numerous industries, including construction, electrical, and plumbing. The material's lightweight nature combined with its strength and flexibility allows it to be molded into different forms, such as pipes, sheets, and films, broadening its usage spectrum.
However, PVC has come under scrutiny due to environmental and health concerns. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has highlighted the potential risks associated with PVC, particularly its production and disposal processes, which can release harmful chemicals. The material's long-lasting nature poses challenges in waste management, prompting discussions on recycling and its impact on ecosystems. While PVC can be recycled, not all facilities accept it, complicating its lifecycle. As regulations tighten, especially with recent bans on certain PVC applications, the industry is exploring alternative materials and innovative solutions to address these issues while maintaining functionality and performance.
Identifying Common Applications of PVC Across Various Industries
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic that boasts a remarkable range of applications across various industries, from construction to healthcare. In the construction sector, PVC is primarily used for plumbing and drainage pipes, siding, and window frames due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global PVC market is expected to reach $78 billion by 2025, driven largely by the increasing demand for sustainable and cost-effective building materials.
In the healthcare industry, PVC plays a critical role in manufacturing medical devices, including IV bags, tubing, and blood bags. Its biocompatibility and ease of sterilization make it a preferred choice for many medical applications. A study from the Vinyl Institute highlights that over 80% of medical devices incorporating plastics utilize PVC due to its reliability and safety features.
**Tip:** When selecting PVC for your projects, consider its certification for safety and environmental compliance to ensure its suitability for applications, especially in healthcare.
Additionally, in the automotive and electronics industries, PVC is utilized for components such as dashboard covers, wiring insulation, and exterior trims. Its lightweight yet robust nature contributes to improved energy efficiency and performance. According to a report by Research and Markets, the growing trend towards electrification in automobiles is further increasing the demand for PVC materials that can offer flexibility and performance.
**Tip:** Opt for PVC products that are manufactured using recycled materials to minimize environmental impact while still benefiting from the material's versatility and durability.
Exploring the Versatility of PVC Material: Applications, Benefits, and Environmental Impact - Identifying Common Applications of PVC Across Various Industries
| Industry | Common Applications | Key Benefits | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Pipes, windows, siding | Durability, low cost, ease of installation | Energy-intensive production, recyclable |
| Healthcare | Medical gloves, IV bags | Biocompatibility, sterilization capability | Can be made from bio-based sources |
| Automotive | Interior trim, dashboards | Lightweight, resistant to moisture | Recycling options available |
| Packaging | Food wrap, containers | Barrier protection, lightweight | Concerns over disposal and microplastics |
| Electrical | Insulation, cable sheathing | Flame resistance, electrical insulation | Potential leaching of additives |
Evaluating the Environmental Impact of PVC Production and Disposal
The environmental impact of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) production and disposal is a critical topic in today’s discussion on sustainable materials. PVC is one of the most widely produced synthetic plastics, with global production figures reaching approximately 40 million tonnes per year as reported by the PlasticsEurope’s 2020 report. The manufacturing process of PVC involves the use of chlorine and ethylene, which can contribute to pollution if not managed properly. Specifically, the production phase can emit dioxins, which are known to be harmful to both human health and ecosystems.
Moreover, the disposal of PVC presents significant environmental challenges. When incinerated, PVC releases harmful toxins, while in landfills, it can take centuries to decompose, leading to long-term leaching of harmful substances into the soil and groundwater. According to a study by the European Commission, around 50% of PVC products end up in landfills, perpetuating their negative environmental footprint. To address these issues, the industry is increasingly focusing on recycling initiatives, with only about 10% of PVC currently being recycled—a stark contrast to the 30% recycling rate seen in other plastics, as highlighted by the breakdown provided by the European PVC industry. This reinforces the urgent need for improved waste management strategies and technological advancements to mitigate the environmental impact associated with PVC.
Assessing the Benefits of Using PVC in Construction and Manufacturing
 PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is widely recognized for its versatility in construction and manufacturing, offering numerous benefits that make it a popular choice among industry professionals. According to a report by the European PVC Industry, the material accounts for over 20% of the global plastic market, primarily due to its durability, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to corrosion. Its application ranges from pipes and roofing to windows and flooring, providing a reliable solution for both residential and commercial projects.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is widely recognized for its versatility in construction and manufacturing, offering numerous benefits that make it a popular choice among industry professionals. According to a report by the European PVC Industry, the material accounts for over 20% of the global plastic market, primarily due to its durability, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to corrosion. Its application ranges from pipes and roofing to windows and flooring, providing a reliable solution for both residential and commercial projects.
One of the key advantages of using PVC in construction is its low maintenance requirement. Unlike materials such as wood or metal, PVC does not rot, rust, or require regular painting, which can significantly reduce long-term upkeep costs. Additionally, the global construction market has seen an increasing preference for sustainable materials, and PVC can be recycled multiple times without losing its properties, which aligns with eco-friendly initiatives. A recent study indicates that about 55% of PVC products are recycled, highlighting its potential for reducing waste in the industry.
Tips for Using PVC:
- When selecting PVC products, ensure they meet local building codes to guarantee safety and performance.
- Consider the life cycle of the materials; choosing recycled or recyclable PVC can contribute to sustainability goals for your projects.
- Evaluate the specific grade of PVC needed for your application to maximize durability and effectiveness.
Exploring Sustainable Alternatives and Innovations in PVC Recycling Processes
The quest for sustainable alternatives to conventional PVC (polyvinyl chloride) has gained momentum, urging innovation in recycling processes to mitigate environmental impacts. Traditional PVC recycling mechanisms often face challenges due to the material's complex composition, which can complicate the recycling process and lead to contamination. However, recent advancements have introduced novel techniques that enhance the efficiency of PVC recycling. For instance, chemical recycling methods, which break down PVC into its monomer components, are emerging as a viable option. This not only allows for the recovery of pure raw materials but also reduces the reliance on virgin resources.

Moreover, the development of bio-based PVC alternatives has garnered attention as a promising route towards sustainability. These materials, derived from renewable sources, aim to mimic the properties of traditional PVC while minimizing environmental footprint. Innovations in material science are facilitating the creation of biodegradable or more easily recyclable options that can help address the challenges posed by plastic waste. The integration of improved recycling practices with the introduction of sustainable alternatives could pave the way for a more circular economy in the PVC industry, ultimately leading to reduced ecological impact and enhanced resource efficiency.
Related Posts
-
Exploring the Versatility of PVC Plastic: Innovative Applications in Modern Design
-

Exploring the Versatility and Applications of PVC Film in Modern Industries
-

7 Amazing Benefits of Using PVC Material in Modern Manufacturing
-

7 Reasons Why Polypropylene Injection Molding is the Best Choice for Your Project
-

How to Optimize Your Production Process with Poly Plastic Solutions
-

What is Poly Plastic and How it Revolutionizes Packaging Solutions in 2023
